How Do We Know The Makeup Of Blood Cells
Blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue instead of only a fluid? It is composed of living cells suspended in plasma, the liquid that makes up around 55% of the blood. Plasma transports blood cells, proteins, electrolytes, hormones, and nutrients throughout the body. It too brings waste products from the body tissues to the urinary system, where the kidneys filter them out of the blood. There are three broad categories of blood cells that have important functions. Scarlet claret cells, or erythrocytes, conduct oxygen from the lungs out to the balance of the body. White claret cells, or leukocytes, assistance protect the body from pathogens. There are 5 different types of leukocytes that combat infection in different ways. Platelets, or thrombocytes, clump together and grade clots to repair torn claret vessels. Blood has 5 principal functions that go far essential for a person'south survival: Red bone marrow contains hematopoietic stem cells, or hemocytoblasts, which divide and differentiate into myeloid and lymphoid stem cells. Myeloid stem cells give rise to red blood cells, platelets, and myeloblasts—cells that differentiate into myeloid white blood cells: neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and monocytes. Lymphoid stem cells requite rise to lymphoblasts, which differentiate into white blood cells classified equally lymphocytes: B cells, T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. Myeloid white blood cells are the mature, differentiated forms of myeloblasts in the carmine os marrow. In that location are two varieties of myeloid white blood cells: granular and agranular. Granular myeloid white blood cells include neutrophils (the most numerous type of white claret prison cell), basophils, and eosinophils. These types of white blood cells have granules in their cytoplasm and nuclei with multiple lobes. In contrast, monocytes are agranular myeloid white blood cells. They exercise not accept cytoplasmic granules, and their nuclei are not lobed. Lymphoid white blood cells are the mature, differentiated forms of lymphoblasts, which are descended from lymphoid stem cells in the cherry-red bone marrow. Lymphoid white blood cells are called lymphocytes, a category which includes B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells. Like monocytes, B and T lymphocytes are agranular, and their nuclei are not lobed. NK cells are granular—in fact, they are often referred to every bit large granular lymphocytes.What is Blood?
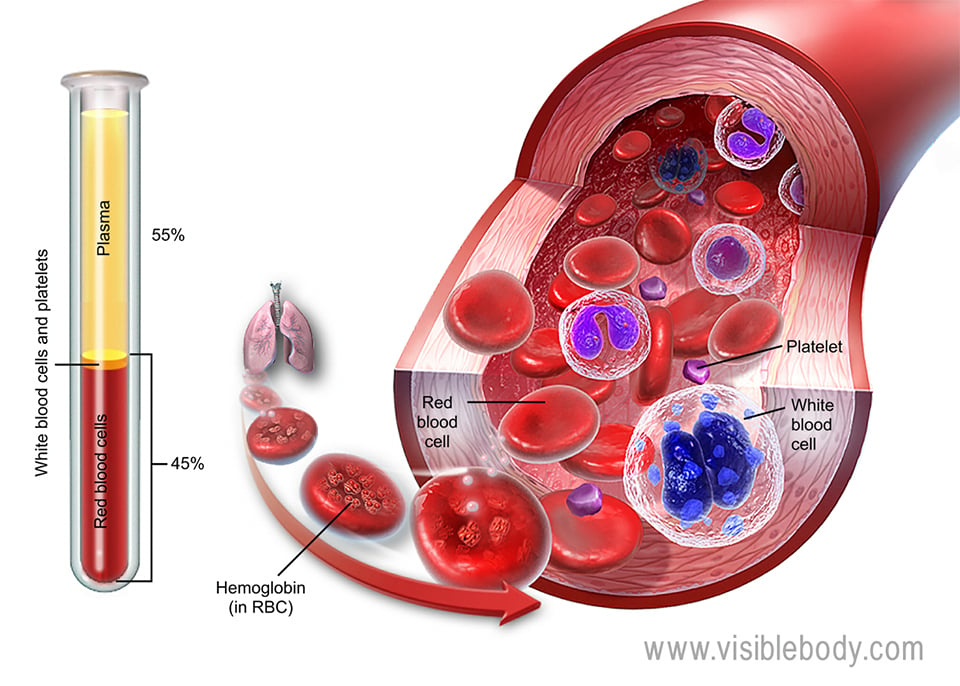
Red blood cells and platelets

1. Blood is fabricated upwardly of 55% plasma and 45% formed elements—ruddy blood cells, white claret cells, and platelets.
two. Blood has five main functions.
three. Blood cells are produced within red bone marrow.
4. There are 5 types of white blood cells: neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes.
Granular myeloid white blood cells



Source: https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/biology/blood-cells/blood-overview
Posted by: williamsawfut1966.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Do We Know The Makeup Of Blood Cells"
Post a Comment